Onion-like carbon
Carbon onions are quasi-spherical nanoparticles consisting of fullerene-like carbon layers enclosed by concentric graphitic shells. They are predicted to have properties different from other carbon nanostructures as graphite, nanodiamond or nanotubes due to their highly symmetric structure and may serve use in different applications.
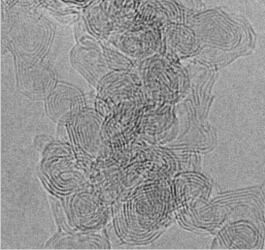
HRTEM image of carbon onions.
Several recent publications have shown that magnetic nanoparticles encapsulated within graphite-like layers may find applications as components of magnetic recording systems [1], magnetic fluids [2], electromagnetic shielding materials [3]. Carbon onions can even serve as nanocapsules for drug delivery systems - the external graphite layers providing protection to substances contained within and can serving as a template for the attachment of desirable functional groups. Until recently the investigation of the unique chemical and physical properites of carbon onions was limited by the lack of a method which produced them with well ordered structures and in sufficiently large quantities. Now several methods exist such as one which forms onion-like structures by annealling nanodiamond 1000 – 1800 K (see below).
In the Group we are investigating the physical and chemical properties of these multishelled carbon onions by a combination of microscopy and spectroscopic methods.
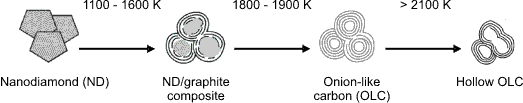
Illustration showing the transformation steps of nanodiamond to onion-like carbon.
Current work has included photoemission studies on the effects of incalating carbon onions with potassium which showed how the electronic structure bears a closer resemblance to graphite than fullerene carbon. Further work has studied the composition of nanodiamond-onion phase change products as a function of temperature.
Our Publications
- Brieva AC, Jager C, Huisken F, Siller L, Butenko YV
A sensible route to covalent functionalization of carbon nanoparticles with aromatic compounds
CARBON 47 (12): 2812-2820 OCT 2009 - Butenko Yu V, Chakraborty A K, Peltekis N, Krishnamurthy S, Dhanak VR, Hunt MRC, Siller L
Potassium intercalation of carbon onions ‘opened’ by carbon dioxide treatment
CARBON 133 1573-1580 JUL 2008 - Montalti M, Krishnamurthy S, Chao Y, et al.
Photoemission spectroscopy of clean and potassium-intercalated carbon onions
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 67 (11): Art. No. 113401 MAR 15 2003
- Butenko YV, Krishnamurthy S, Chakraborty AK, et al.
Photoemission study of onionlike carbons produced by annealing nanodiamonds
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 71 (7): Art. No. 075420 FEB 2005
References
- Subramoney S. Novel nanocarbons - structure, properties, and potential applications. Adv Mater 1998;10(15):1157-71.
- Caiulo N, Yu CH, Yu KMK, Lo CCH, Oduro W, Thiebaut B, Bishop P, Tsang SC. Carbon-decorated FePt nanoparticles. Adv Funct Mater 2007;17(8):1392-6.
- Che RC, Peng LM, Duan XF, Chen Q, Liang XL. Microwave absorption enhancement and complex permittivity and permeability of Fe encapsulated within carbon nanotubes. Adv Mater 2004;16(5):401-5.

