Lee Borthwick bring contribution on PNAS paper
Lee Borthwick contributes to a new publication in PNAS
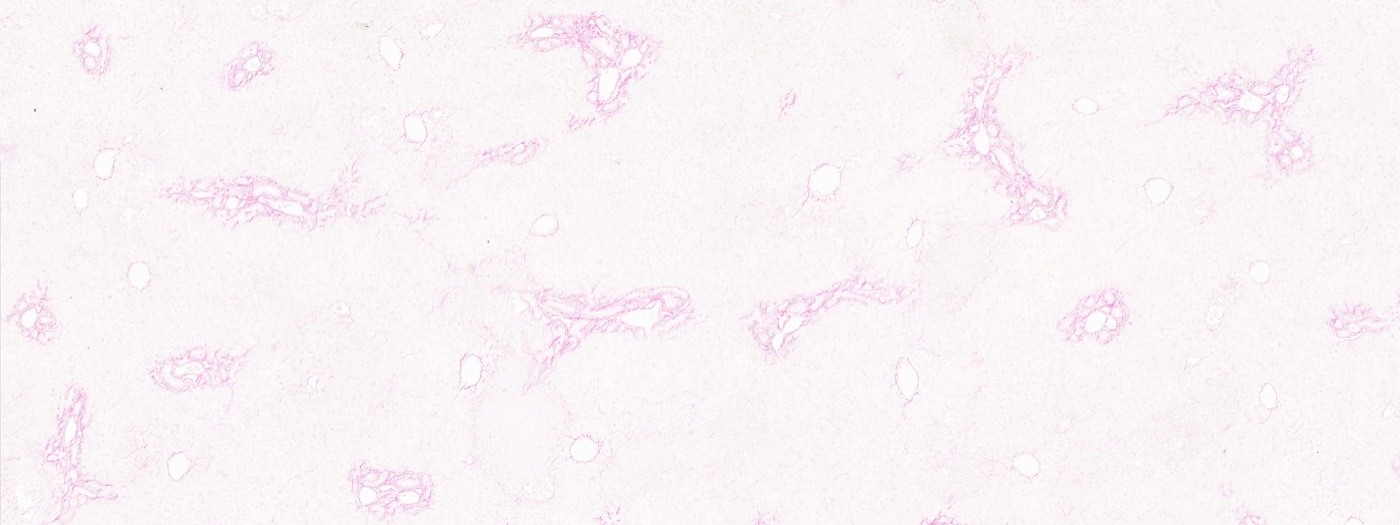
Lee Borthwick has recently contributed to a research lead by Dr. John Blaikley from the University of Manchester resulting in a new publication in PNAS, entitled:
The circadian clock protein REVERBα inhibits pulmonary fibrosis development
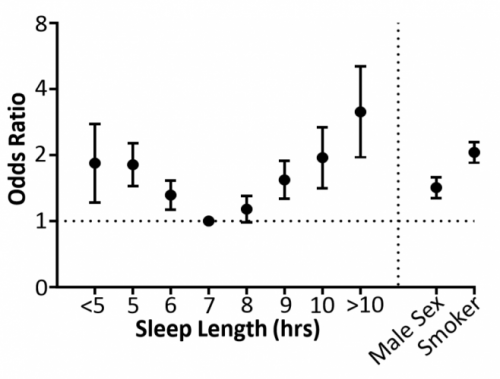
This research shows that "people who regularly sleep for long (≥11h) or short (≤4h) periods are 2-3 times more likely to have the incurable disease, pulmonary fibrosis, compared to those that sleep for 7 hours in a day. They attribute this association to the body clock"
Click HERE to read the paper on the publisher's website and download a pdf version of the publication.
Click HERE to read the press release on the website of University of Manchester

Last modified: Mon, 06 Jan 2020 15:43:42 GMT
