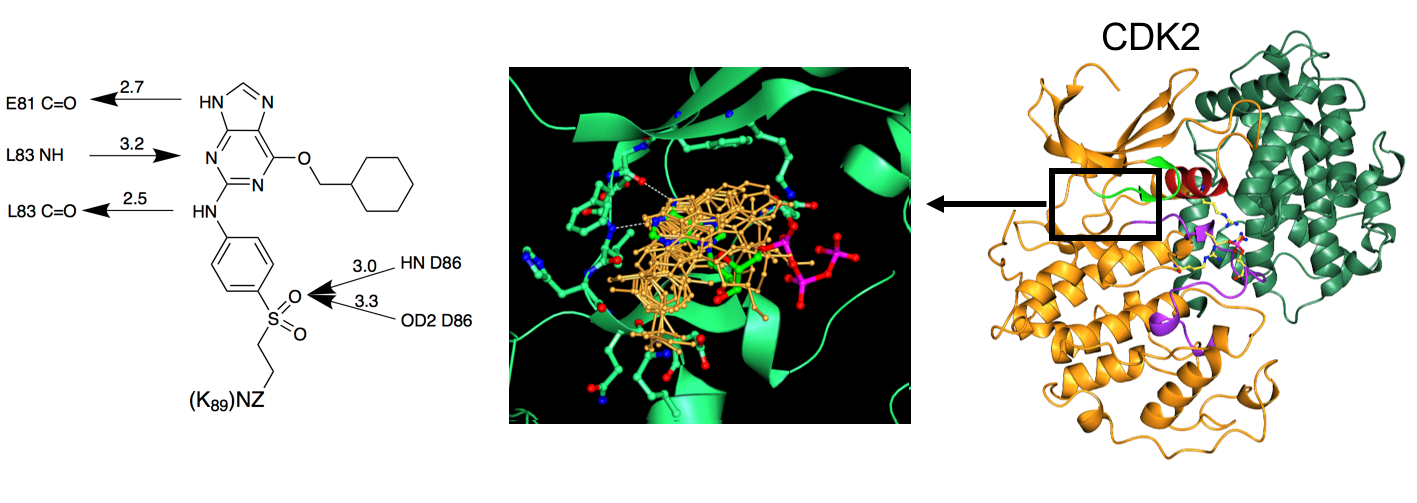
Development of CDK2 inhibitors
Chemical-genetic evidence has shown a difference in the cellular response to the absence of CDK2 and to small-molecule CDK2 inhibitors suggesting that CDK2 inhibitors may be appropriate for treating a subset of tumours with defined genetic characteristics. Strategies that exploit synthetic lethalities have also highlighted a potential role for CDK2 inhibitors in the clinic. We have determined a number of CDK2-cyclin A- inhibitor co-complex structures that have aided the design of selective CDK inhibitors targeting the ATP binding site. These inhibitors mimic the interactions made by the authentic ligand ATP including crucially hydrogen bonds made by the adenine ring with backbone carbonyl and amide moieties in the CDK hinge sequence that links the lobes of the kinase fold. Further interactions exploit regions within the active site beyond where ATP binds and sequence differences outside of the active site cleft on the surface of the C-terminal lobe.
Highlights
- Potent and selective ATP-competitive CDK2 inhibitors have been developed using structure-lead approaches
- Irreversible inhibitors have a distinctive mode of action and offer an alternative route to competitive ATP inhibitors to target protein kinases.
Collaborators: Colleagues at the NICR; Dr Aude Echalier-Glazer, Exscientia; Dr Laurent Meijer, ManRos Therapeutics, Roscoff.
PDB entries: 5CYI, 1W8C, 4CFN, 4CFM, 4CFV, 4CFU, 4CFX, and 4CFW, 3LQ5
Associated publications:
Identification and Characterization of an Irreversible Inhibitor of CDK2, (2015) Anscombe et al., Chem. Biol. 22: 1-6.
8-Substituted O6-Cyclohexylmethylguanine CDK2 Inhibitors; Optimisation of an Alternative Binding Mode Utilising Structure-Based Inhibitor Design, (2013) Carbain et al., J. Med. Chem., 57:56-70.
CDK Inhibitors Roscovitine and CR8 Trigger Mcl-1 Down-Regulation and Apoptotic Cell Death in Neuroblastoma, (2010) Bettayeb, et al., Genes Cancer 1: 369-380.
Meriolins, a new class of cell death inducing kinase inhibitors with enhanced selectivity for cyclin-dependent kinases, (2007) Bettayeb, et al., Cancer Res 67: 8325-8334.