News
New Paper - Structure-based design of MDM2 inhibitors
Structure-based design of potent and orally active isoindolinone inhibitors of MDM2-p53 protein–protein interaction
J. Med. Chem., 2021, 64, 4071–4088
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c02188
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c02188
Gianni Chessari*, Ian R. Hardcastle*, Jong Sook Ahn, Burcu Anil, Elizabeth Anscombe, Ruth H. Bawn, Luke D. Bevan, Timothy J. Blackburn, Ildiko Buck, Celine Cano, Benoit Carbain, Juan Castro, Ben Cons, Sarah J. Cully, Jane A. Endicott, Lynsey Fazal, Bernard T. Golding, Roger J. Griffin, Karen Haggerty, Suzannah J. Harnor, Keisha Hearn, Stephen Hobson, Rhian S. Holvey, Steven Howard, Claire E. Jennings, Christopher N. Johnson, John Lunec, Duncan C. Miller, David R. Newell, Martin E. M. Noble, Judith Reeks, Charlotte H. Revill, Christiane Riedinger, Jeffrey D. St. Denis, Emiliano Tamanini, Huw Thomas, Neil T. Thompson, Mladen Vinković, Stephen R. Wedge, Pamela A. Williams, Nicola E. Wilsher, Bian Zhang, Yan Zhao
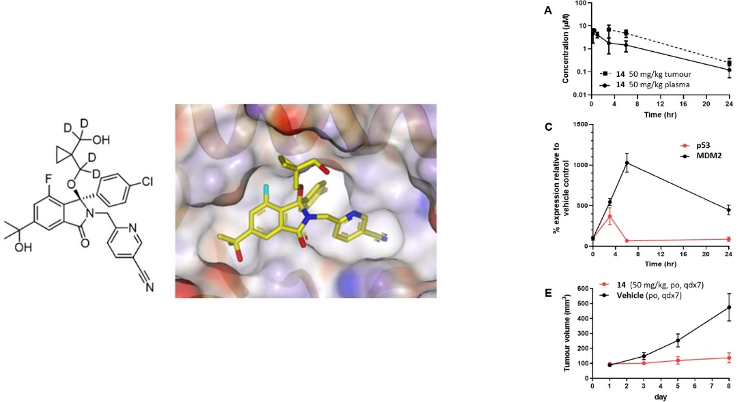
This work, undertaken as part of our strategic Drug Discovery Alliance with Astex Pharmaceuticals (UK), describes the structure-guided design of novel isoindolinone-based MDM2 inhibitors. Determination of the first isoindolinone-MDM2 X-ray crystal structure was key to determining the subsequent lead optimisation strategy and further extensive X-ray crystallography was used to understand ligand binding modes.
The application of structure-aided and ligand-based design, together with metabolite identification, allowed the challenges of chemical and metabolic stability to be overcome, enabling MDM2 binding affinity and oral bioavailability to be optimised.
Modulation of the electronic character of the isoindolinone system by incorporation of fluorine greatly reduced the propensity for C3 side chain elimination and application of the deuterium isotope effect to these molecules proved a successful strategy for reducing CYP3A4-mediated oxidation of metabolically labile sites. Two compounds are described which show the best balance of properties (potency, selectivity, and oral bioavailability) and were used to demonstrate in vivo pharmacodynamic effects and antitumor efficacy in the SJSA-1 xenograft model at doses which were well tolerated. In summary, potent, selective, and orally efficacious inhibitors of the p53-MDM2 protein–protein interaction were identified.
Last modified: Mon, 19 Dec 2022 17:24:58 GMT