News
New Paper - DNA-compatible SNAr reactions
Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2022, 63, 116688
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2022.116688
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/ S0968089622000803
Isaline F. S. F. Castan, Andrew Madin, Garry Pairaudeau and Michael J. Waring*
DNA-encoded chemical library (DEL) technology represents a powerful method to identify hit compounds in drug discovery campaigns and is now competitive with more widely employed approaches, such as high throughput screening.
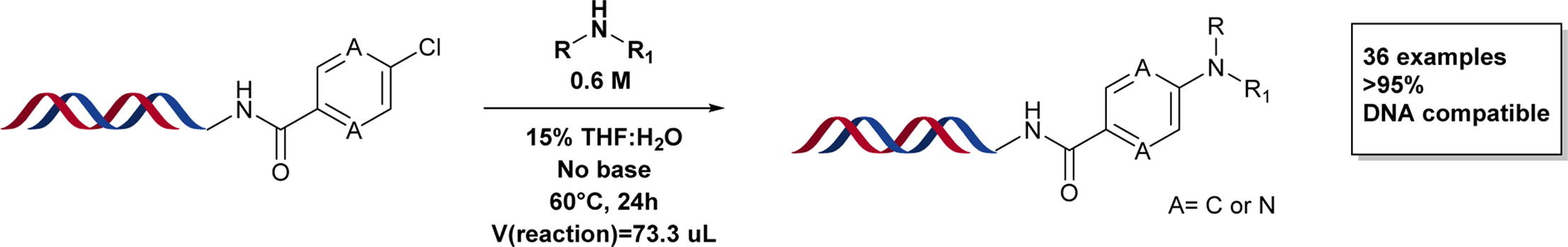
Nucleophilic aromatic substitution (SNAr) is reported to be the third most used chemical reaction for the production of bioactive molecules. However, methodologies for on-DNA SNAr reactions are limited. This work explored optimal conditions for on-DNA SNAr reactions across a range of substrates with differing reactivity.
Entirely the work of Medicinal Chemistry PhD student Isaline Castan (as part of an ongoing collaboration with AstraZeneca), the new methodology presents a significant advancement for DEL construction on poorly activated scaffolds. The optimised procedure for the SNAr reaction was established using factorial experimental design (FED) on-DNA and comprises longer reaction time (24 h), with 15% THF as a co-solvent, no micellar surfactant, organic concentration fixed at 0.6 M and temperature at 60 °C. This method gave conversions of >95% for pyridine and pyrazine scaffolds for 36 secondary cyclic amines and scope on other amines is also described.
This work provides grounds for improving DEL synthesis, allowing more informed selection of reagent pairs in library design, thus increasing the fidelity and diversity of DELs. This study defines the current limits for SNAr reactions for poorly activated heteroarene electrophiles and amine nucleophiles.
Last modified: Mon, 19 Dec 2022 17:16:26 GMT