Glossary
Glossary of terms:
A
An Allele
Each gene has two alleles. One comes from your mother and one from your father. Alleles are different forms of a gene.

This is an image of DNA. DNA contains a huge number of genes.
The APOE ε4 allele
For the APOE gene the main types of alleles are ε2, ε3 and ε4. If you have the ε4 allele you are at greater risk of dementia. If you have 2 copies( one from your mother and one from your father) of the ε4 allele, then you are at an even greater risk than just having 1.
B
C
The Cambridge Cognitive Examination (CAMCOG)
This is a paper and pencil test taken from ‘The Revised Cambridge Examination for Mental Disorders of the Elderly’ (CAMDEX). See picture. The CAMCOG tests many functions of the brain. These are:
- Orientation (what the time and date is and what is around us)
- Naming objects
- Memory
- Concentration
- Maths
- Drawing and Recognising objects
- Executive function (problem solving)
- Understanding language.

This is a photographic image of the CAMDEX-R. The CAMCOG is found within this book.
From this, the scores from each section are added up. The maximum score is 107. This score is then compared to a normal score for somebody of that age without a stroke so that scientists will know if a score is normal or not.
A lower brain test score than normal would suggest lower brain function. A person may have a very low score in a particular section and this can suggest they have a problem in that area. For example, a low score on the memory section suggests problems with memory.
A CAMCOG test can be repeated yearly, if peoples brain test scores are lower than before this tells us that their brain function is deteriorating. It is important to remember that as we age, it is normal for brain function to slowly lower. However, if brain test scores are lowering faster than normal, this could lead to developing dementia.
Cardiovascular risk factors
Cardiovascular risk factors affect our cardiovascular system. Cardiovascular risk factors are factors that damage our blood vessels and make our cardiovascular system less healthy. The damage is usually through gradual damage of blood vessels.
Examples of these are:
- smoking
- high blood pressure
- diabetes
- heart disease
- Atrial fibrillation – (a condition that causes an irregular heart beat)
The cardiovascular system
This system allows us to receive and transport blood, gases and nutrients to all areas of the body to maintain health.
D
Dementia:This happens when damage to our brain function is severe enough that it affects our daily life. A patient with dementia may feel that they have problems with memory, organising, attention, understanding language and may feel confused.
There are different types of dementia, in the COGFAST studies, scientists looked at:
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Vascular dementia
- Mixed dementia
Alzheimers disease occurs when the brain is damaged, particularly in the hippocampus causing memory problems.
Vascular dementia is due to problems with the supply of blood to the brain which may have been caused by a stroke or a collection of small strokes.
Mixed dementia is where you can have more than 1 type of dementia.
Depression
It is usually described as a low mood disorder. It can affect people in lots of ways for example, people may feel like they are always tired, hopeless, sad, tearful and stressed.
A depression score could help grade low mood, and help decide if low mood has progressed to depression which needs help. Click here to a a short depression self-assessment. This is for information only and is not intended to replace a consultation with a GP.
Depressive symptoms
A person can experience depressive symptoms such as low mood but it is not severe enough to be depression.
E
F
G
A Gene
A gene is a section of DNA that gives a person a particular characteristic.
H
The hippocampus
The is found in the middle of the brain and is important for learning and memory. The name ‘hippocampus’ comes from the ancient Greek word for sea horse. It was given this name as it is similar shape to a seahorse. The hippocampus is split up into areas called CA1, CA2 and CA3 and CA4.
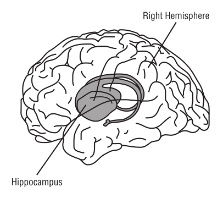

This is a diagram of the brain This is an image of a seahorse, which is a similar shape to the hippocampus.
I
J
K
L
M
The Medial temporal lobe
It is in the middle of the brain and is important for learning and memory. Medial temporal atrophy occurs when the medial temporal lobe shrinks.
N
Neuroimaging
This is a way that we can take pictures of the brain. A type of neuroimaging is magnetic resonance imagining (MRI). MRI scans let us look at sizes of different parts of the brain.
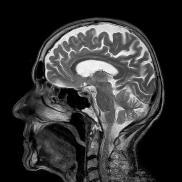
This image is an MRI scan of a normal brain
Neuron
There are around 86 billion neurons in the human brain. Neurons are nerve cells that receive and send messages in the brain.
This image is of a neuron
O
P
Q
R
S
A stroke
This happens when a large blood vessel in the brain becomes blocked or there is a bleed and this causes a circulation problem. When insufficient blood gets to the brain, the brain cells do not get enough oxygen and can die. A stroke causes brain damage which results in lower than normal brain function. It causes sudden symptoms that lasts over 24 hours. A person who has had a stroke could be affected in a number of ways depending on how bad the damage is and where it is in the brain. Sometimes the brain overcomes the circulation problem quickly and the damage is minimal. Sometimes the blockage is more severe and in these cases the effects are more severe and permanent. Strokes can cause a number of symptoms including problems with movement or swallowing, speech difficulties and confusion.
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z